
SDN’s Best of 2022
As we approach the end of 2022, we wanted to share some of the Student ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: December 22, 2022

As we approach the end of 2022, we wanted to share some of the Student ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: December 22, 2022
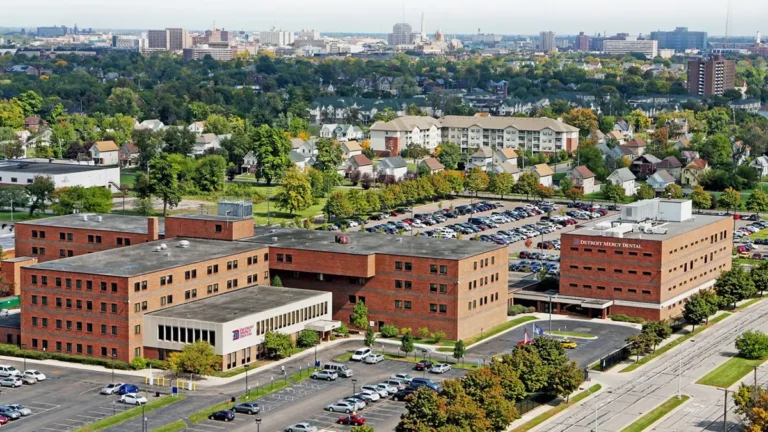

Dr. Steven Chang (he/him/his) is the Director of Admissions at the University of Detroit Mercy ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: December 15, 2022

In Part 1, I introduced you to some of the results from the 2022 SJT ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: December 8, 2022

What are students encountering as they take situational judgment tests? This is the first of ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: December 1, 2022

Are you a busy prehealth or health professional student – or are you shopping for ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: November 24, 2022

Most rural Americans face significant challenges accessing healthcare. There are major shortages of physicians, dentists, ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: November 17, 2022

Dr. Choukalas is an academic anesthesiologist and intensive care physician. He is Co-PI on a ... Read more
Written by: Student Doctor Network
Published on: November 9, 2022

As a health professions advisor and admissions professional, I have found myself connecting with the ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: November 3, 2022

Transitioning from medical school to residency marks one of the biggest changes in your medical ... Read more
Written by: Dr. Brennan Kruszewski
Published on: October 21, 2022

The cost of attending medical school, and other health professional programs, has increased dramatically over ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: September 23, 2022
Robert Nadeau DDS, MD is in his seventh year at the University of Minnesota School ... Read more
Written by: Student Doctor Network
Published on: September 8, 2022

If you want the unvarnished truth about your medical school chances, Goro is the person ... Read more
Written by: Student Doctor Network
Published on: September 1, 2022

I often use the “marathon” metaphor when it comes to the timeline from preparing your ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: August 25, 2022

Undergraduate and post-baccalaureate educational institutions want their students to succeed, so they invest in advising ... Read more
Written by: Emil Chuck, PhD
Published on: August 10, 2022

NRMP would eliminate the SOAP in favor of a two-phase main residency match The National ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: August 4, 2022

There are various ways to help you pay for college, including grants, scholarships, savings, and ... Read more
Written by: Student Doctor Network
Published on: August 3, 2022

On March 1, 2022, the Liason Committee on Medical Education (LCME) updated the Accreditation Status ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: March 2, 2022

CNUCOM Remains in Provisional Accreditation Status; Reconsideration Hearing Scheduled February 17 On January 31, 2022, ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: February 2, 2022

Premed and other pre-health students have struggled during the COVID-19 pandemic to find and participate ... Read more
Written by: Laura Turner
Published on: January 31, 2022